Do you want to lower your energy bills and help the environment? Knowing how to check the energy efficiency of your air conditioner is crucial for every homeowner. Here’s a quick answer before we dive deeper:
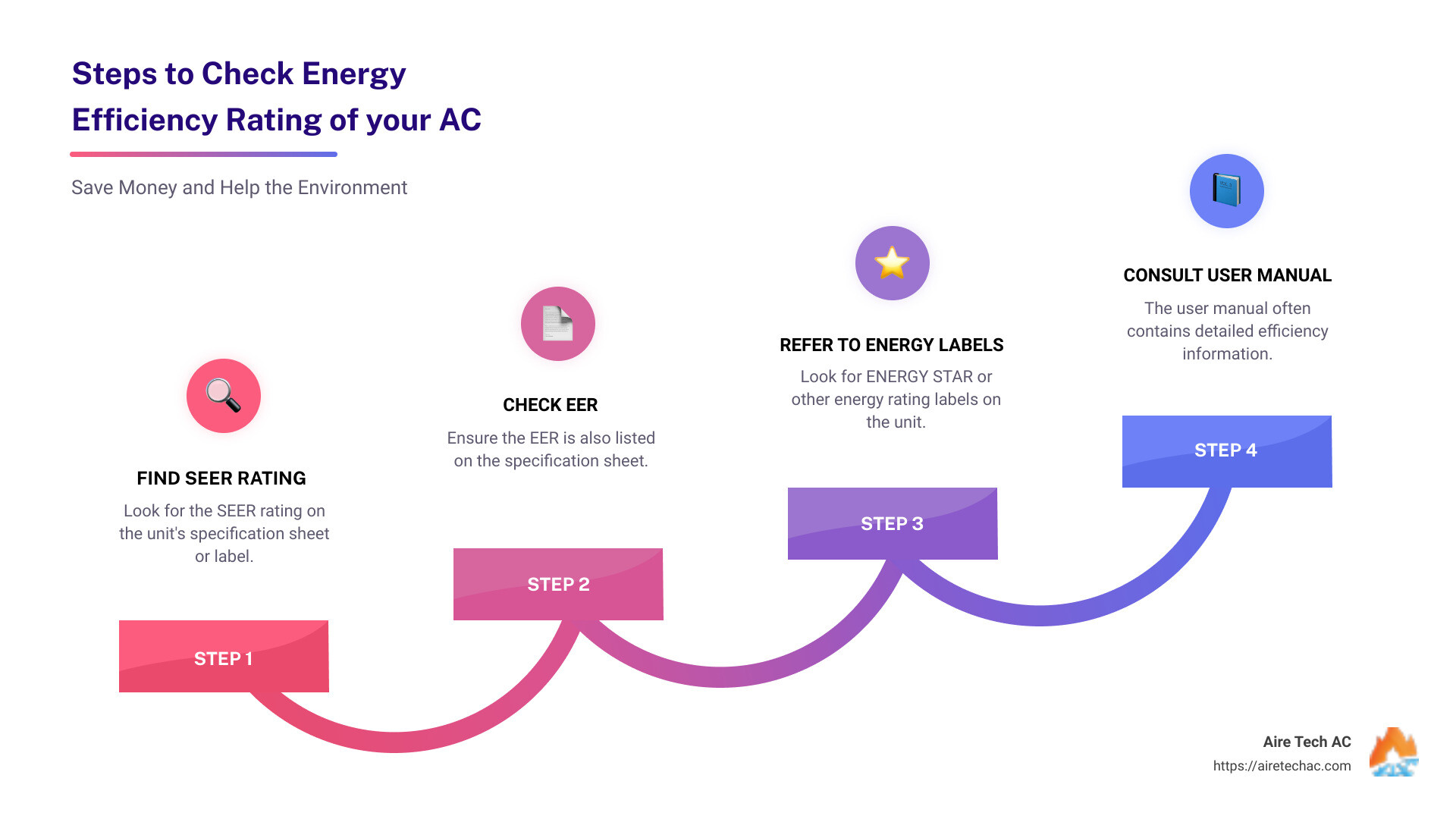
- Look for the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating: Found on the unit’s specification sheet or label.
- Check the EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): This is also listed on the specification sheet.
- Refer to energy rating labels: Such as ENERGY STAR ratings.
- Consult the user manual: It often contains detailed efficiency information.
Air conditioning units can be a significant source of energy consumption, especially during those scorching summer months. Having an energy-efficient unit can make a substantial difference in your household’s overall energy usage and bills. By choosing a system with a high energy efficiency rating, you’ll save money in the long run and reduce your carbon footprint.
Energy efficiency is not just a technical term; it translates into real savings and a more comfortable home environment. At Aire Tech AC, we believe in empowering our customers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their HVAC systems.
Understanding Energy Efficiency Ratings
When it comes to your HVAC system, understanding energy efficiency ratings can save you a lot of money. Let’s break down the key terms you need to know: SEER, EER, and AFUE.
What is SEER?
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. This rating measures how efficiently an air conditioner converts electricity into cooling power over an entire cooling season.
Higher SEER ratings mean better efficiency. For instance, a unit with a SEER of 20 is more efficient than one with a SEER of 14.5, which is the minimum required to meet the U.S. Department of Energy’s ENERGY STAR standards.
What is EER?
EER, or Energy Efficiency Ratio, measures the efficiency of an air conditioner at a specific, constant temperature. Unlike SEER, which averages efficiency over a season, EER provides a snapshot of performance under set conditions.
For example, if an AC unit has a cooling capacity of 10,000 BTUs and uses 1,000 watts, its EER is 10. Higher EER ratings indicate better energy efficiency.
What is AFUE?
AFUE stands for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. This rating applies to furnaces and measures how efficiently they convert fuel into heat over a year.
An AFUE of 90% means that 90% of the fuel becomes heat, while the remaining 10% is lost. A furnace with an AFUE of 95% or higher is considered highly efficient.
Key Terms Explained
- BTU: British Thermal Unit, a measure of heat. One BTU is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
- kW: Kilowatt, a unit of power. One kilowatt equals 1,000 watts.
- ENERGY STAR: A certification indicating that a product meets energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Understanding these ratings can help you choose the most energy-efficient HVAC system for your home, ultimately saving you money and reducing your environmental impact.
How to Check Energy Efficiency of Air Conditioner
Calculating SEER and EER
To check the energy efficiency of your air conditioner, you’ll want to look at its SEER and EER ratings.
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures how efficiently an AC unit operates over a typical cooling season. EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures efficiency at a single operating condition.
Here’s how you can calculate these ratings:
- Find the SEER Rating:
- Check the user manual or the specification sheet of your AC unit.
- You can also find it on the AC unit cabinet.
- Formula: SEER = Total BTUs over a season / Total watt-hours over a season.
- Find the EER Rating:
- Look for the EER on the same user manual, specification sheet, or the AC unit cabinet.
- Formula: EER = Capacity (in BTU) / Power (in W).
Example Calculation for EER:
Let’s say you have a 14,000 BTU mini split air conditioner powered by 1,400W.
EER rating = 14,000 BTU / 1,400W = 10
This means the AC provides 10 BTUs of cooling for every watt of energy supplied.
Recommended Ratings:
– Aim for a SEER of at least 14.5 to meet ENERGY STAR guidelines.
– Aim for an EER of at least 14 for good energy efficiency.
Using COP for kW Rated Units
For air conditioners with cooling capacity rated in kW, you’ll use the Coefficient of Performance (COP) instead of EER.
Formula for COP:
COP = Cooling capacity (kW) / Power input (kWh)
Example Calculation for COP:
If an AC unit has a cooling capacity of 5 kW and uses 1.25 kWh of power:
COP = 5 kW / 1.25 kWh = 4
A COP higher than 4 is considered good. To convert COP to EER, multiply by 3.4.
Standard Parameters:
– Relative Humidity: 50%
– Outdoor Temperature: 95°F (35°C)
– Indoor Temperature: 80°F (26.7°C)
These calculations assume standard conditions and full load operation. Real-world efficiency may vary.
Signs Your AC Isn’t Energy Efficient
Out of Control Interior Humidity
One sign your air conditioner isn’t energy efficient is if your home feels more humid than usual. A good AC should cool and dehumidify your space. If it’s not, you might have dirty coils.
Dirty Coils: Dust and dirt on coils make it harder for your AC to cool and remove moisture. Clean coils at the start of each cooling season. For interior evaporator coils, hire a professional technician for a thorough cleaning.
Dehumidifying Issues: Increased humidity not only makes the air feel sticky but also means your AC is working harder, costing you more.
Cleaning Tips: Regularly clean or replace air filters. Ensure that coils are free from dust and debris. This helps maintain efficiency.
Higher Utility Bills
A sudden spike in your electricity bill is another red flag. While slight increases over time are normal, a big jump signals trouble.
Review Past Bills: Compare your current bills with those from previous years. Look for unusual increases.
Technician Inspection: If you notice a significant rise, call a local service technician. They can check if your system is running efficiently or if there’s a hidden issue.
Frequent HVAC Breakdowns
If your AC frequently breaks down, it’s likely not running efficiently.
Maintenance Schedule: Regular maintenance can prevent many issues. Follow a schedule for cleaning and servicing your system.
Repair Frequency: If you’re on a first-name basis with your repair technician, it might be time to consider a replacement. Frequent repairs add up and indicate that your system is failing.
Replacement Considerations: Investing in a new, energy-efficient HVAC system can save you money in the long run. Older systems often cost more in repairs and higher utility bills.
Regular checks and maintenance can help you catch these signs early, ensuring your AC runs efficiently and keeps your home comfortable.
Tips for Maintaining Energy Efficiency
Condenser Location
Shade Trees: Placing your outdoor condenser unit in the shade can greatly improve efficiency. Shade trees on the north side of your house are ideal. This helps your AC run more efficiently on hot summer days.
North Side: If possible, install your condenser on the north side of your house. This side gets the least direct sunlight, keeping the unit cooler and more efficient.
Clear Space: Keep the area around the condenser clear of weeds, vines, and other plants. High plant growth can block airflow, reducing efficiency.
Regular Service Checks
Seasonal Checks: Make sure you have your air conditioner cleaned and serviced before the start of intense summer heat. Similarly, have your furnace checked before winter. This ensures your system is ready to handle extreme temperatures.
Cleaning: Dirty coils can reduce your AC’s efficiency. Clean the coils at the beginning of every cooling season. For interior evaporator coils, work with a local service company for thorough cleaning.
Servicing: Regular servicing can catch small issues before they become big problems. This includes checking electrical connections, refrigerant levels, and overall system performance.
Proper Insulation
Air Sealing: Efficient operation of any air conditioning system relies on a properly insulated and air-sealed home. This prevents cool air from escaping and hot air from entering.
Home Energy Assessments: Conduct a home energy audit to identify areas where you can improve insulation and sealing. This can include checking for leaks around windows, doors, and ducts.
Detecting Air Leaks: Use methods like blower door testing and infrared imaging to find and seal air leaks. This helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature and reduces the workload on your AC.
Thermostat Settings
Optimal Settings: Set your air conditioner’s thermostat as high as is comfortably possible in the summer. The less difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures, the lower your cooling bill will be.
Avoid Excessive Cooling: Don’t set your thermostat at a colder setting than normal when you turn on your AC. It won’t cool your home faster and could result in excessive cooling and higher costs.
Fan Speed: Set the fan speed on high, except on very humid days. On humid days, set the fan speed on low for more comfort and better moisture removal.
By following these tips, you can maximize the efficiency of your air conditioner, saving money and keeping your home comfortable.
Frequently Asked Questions about Energy Efficiency Ratings
What is a good SEER rating for an air conditioner?
A good SEER rating (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) for an air conditioner is at least 14.5. This is the minimum standard set by the U.S. Department of Energy for ENERGY STAR certification. Units with higher SEER ratings, such as 20 SEER or more, are even more efficient and can save you more on your utility bills. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the AC unit is, which translates to lower operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
How often should I check my AC’s energy efficiency?
You should check your AC’s energy efficiency at least once a year. Ideally, this should be done during seasonal checks—once in the spring before the cooling season starts and once in the fall before you stop using it. Regular maintenance by a professional technician can help ensure your unit is running efficiently. During these checks, the technician will inspect the SEER rating, clean the coils, check for refrigerant leaks, and ensure all components are functioning correctly.
Can I improve my current AC’s efficiency without replacing it?
Yes, you can improve your current AC’s efficiency without replacing it. Here are some tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean or replace air filters every month or two during the cooling season. Dirty filters can block airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Routine Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks with a professional technician. They can clean the coils, check the refrigerant levels, and ensure the system is running smoothly.
- Minor Repairs: Fixing small issues like leaky ducts, loose electrical connections, or a malfunctioning thermostat can significantly improve efficiency.
- Proper Insulation: Ensure your home is well-insulated to reduce the load on your AC. Check for air leaks around windows and doors and seal them.
By following these steps, you can improve the efficiency of your existing AC unit and save on energy costs without the need for a full replacement.
Call Aire Tech Today!
Checking your air conditioner’s energy efficiency rating is not just a smart move for your wallet, but also for the planet. By understanding and maintaining your AC’s efficiency, you can enjoy several long-term benefits.
Energy Savings
An energy-efficient air conditioner can lower your electricity bills by up to 30%. This means more money in your pocket for other important expenses. Aire Tech AC can help you find and maintain an energy-efficient unit that suits your needs, ensuring you get the most out of your investment.
Long-Term Benefits
While the initial cost of an energy-efficient AC might be higher, the long-term savings on energy bills and maintenance make it a worthy investment. Efficient units tend to last longer and require fewer repairs, saving you money and hassle in the long run.
Environmental Impact
Using energy-efficient air conditioners helps reduce the consumption of fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This contributes to the fight against climate change and helps preserve our environment for future generations.
By choosing Aire Tech AC, you are not only opting for top-notch service but also making a conscious choice for a sustainable future. Our experts can guide you through selecting, installing, and maintaining an energy-efficient air conditioning system that meets your needs.
For more information on how you can maximize your energy savings with an efficient AC unit, visit our service page.
By focusing on energy efficiency, we can all make a difference—both in our homes and for the environment.








